Geospatial Technology for Drones & Unmanned Systems
Find suppliers and developers of Geospatial Technology for Drones & Unmanned Systems, including Drone GIS (Geographic Information Systems), geospatial software, analysis and visualization tools for unmanned 3D mapping, situational awareness and airspace managementGIS Tools for Unmanned Systems
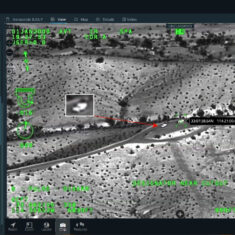
Geospatial software and technology can be used to aid a wide range of UAS (unmanned aerial systems) missions and applications, providing mapping capabilities and situational awareness for both civilian and military drones. Geospatial information can be incorporated into tools for ISR (intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance), command and control (C2), search and rescue, and BVLOS (beyond visual line of sight) missions.
Geospatial Information Applications
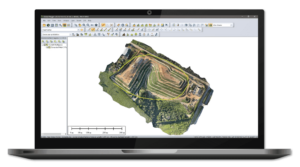
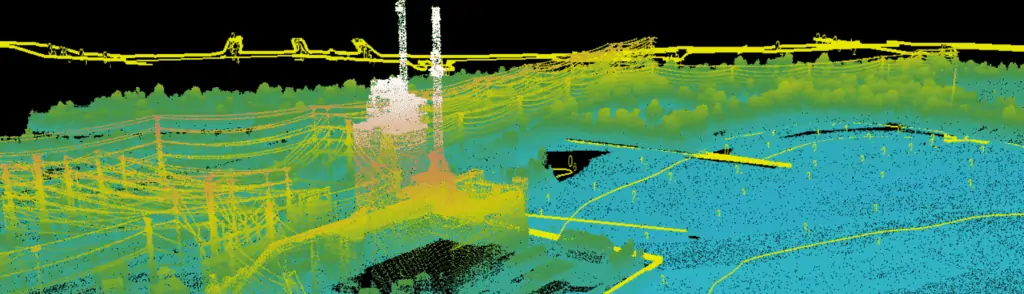
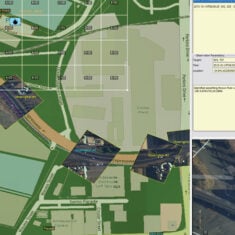
Geospatial data provided by drones and UAS can be used to create multilayered 2D and 3D maps from vector and raster data in a wide variety of formats. Software development kits (SDK) are available that allow developers to package these maps into easy-to-deploy applications, utilizing convenient APIs that do away with the need to develop frameworks from scratch and allow a wide degree of user interface customization. GIS SDK applications may be targeted to a wide range of platforms and form factors, including Windows, Mac, Android, Linux, handheld devices and web browsers.
Geospatial Mapping Tools
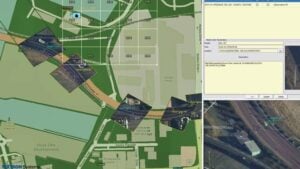
Geospatial mapping tools and GIS (geographic information systems) may allow maps to be overlaid with other sources of data, such as real-time data feeds, images, videos and symbols. For military applications, a MIL-STD 2525 symbol generator may be useful. Large numbers of tracks from UAVs, USVs (unmanned surface vessels), UUVs (unmanned underwater vehicles) and other unmanned systems may be plotted on the map for multi-domain operations control.
Geospatial Software
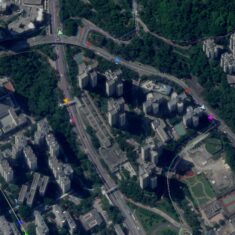
Drone GIS and geospatial software can also be used to create high-accuracy applications that provide airspace awareness for UTM (unmanned traffic management), aiding in the integration of unmanned aircraft into civilian airspace. These applications may be integrated with real-time data feeds such as radar, ADS-B, telemetry and other data sources such as LATAS (Low Altitude Tracking and Avoidance System) feeds, and may provide capabilities such as flight authorization, risk awareness, and geo-fencing.