Autonomous Navigation Software by Inertial Sense Luna
Drone control software allows UAS (unmanned aerial system) operators and pilots to plan and execute missions with both remote-controlled and autonomous aircraft. Typically installed on either a dedicated ground control station (GCS) or a laptop, tablet or mobile phone, the software will use a wireless datalink to communicate with the drone’s autopilot or provide control of the aircraft and its sensor payloads.
UAV control software may integrate payload actions into flight planning, with the ability to take pictures and sensor readings or drop a cargo payload at a predetermined waypoint. Enhanced functionality for photogrammetry missions may also be built into the drone control software, including the ability to calculate an optimal flight path based on camera and survey settings such as GSD (ground sample distance), altitude and overlap
Drone Navigation Software
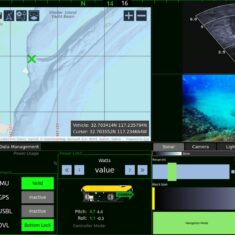
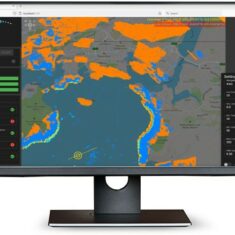
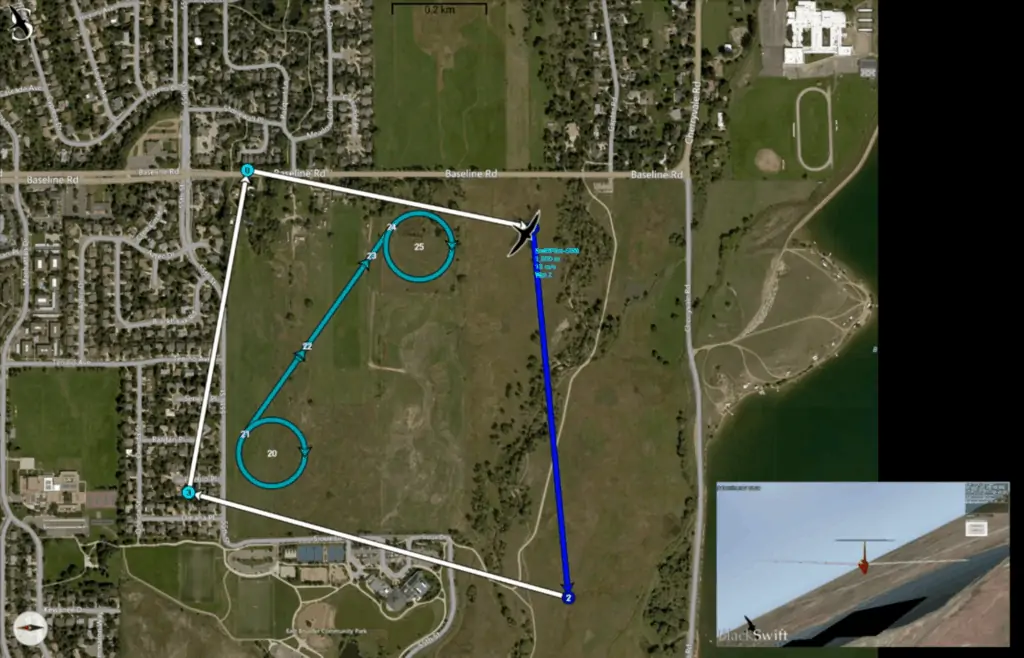
Drone navigation software interfaces will be centred around a digital map that shows the drone’s real-time position in flight, and may also feature overlays of the aircraft’s telemetry data as well as feeds from any sensors. 3D map views may also be available that allow operators to take into account buildings, trees and other obstacles. This functionality is useful for obstacle avoidance as well as for drone missions that involve vertical scanning and imaging.
Drone Navigation Software Applications
UAV navigation software may also allow users to import more detailed map overlays, as well as high-precision DEM (digital elevation model) data. This allows users to account for constantly-changing terrain that may not always be up-to-date on standard maps, and provides more precise terrain following and collision avoidance.
Drone navigation software provides functionality for defining the route taken by a drone during its mission. This will commonly involve selecting waypoints on the map for the drone to follow, or by defining the boundaries of an area that the drone is to survey. The drone may also be programmed to follow certain scan patterns such as corridor mapping, or to operate in different flight modes such as hovering in place or returning to a predefined home location.
Autonomous Navigation Software
Autonomous navigation software may provide automatic geotagging of collected images, synchronising the image timestamps with the autopilot’s GPS data. Many autonomous navigation software platforms will be compatible with RTK GNSS, providing enhanced accuracy for drone mapping and surveying.
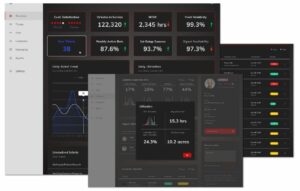
Additional software features that are useful for drone pilots include information about no-fly zones, the ability to request flight authorization under LAANC (Low Altitude Authorization and Notification Capability) or similar schemes, live weather updates, and the ability to record and export log files. Autonomous navigation software may also be part of a larger integrated suite of UAV software that includes fleet management, analytics and other features.