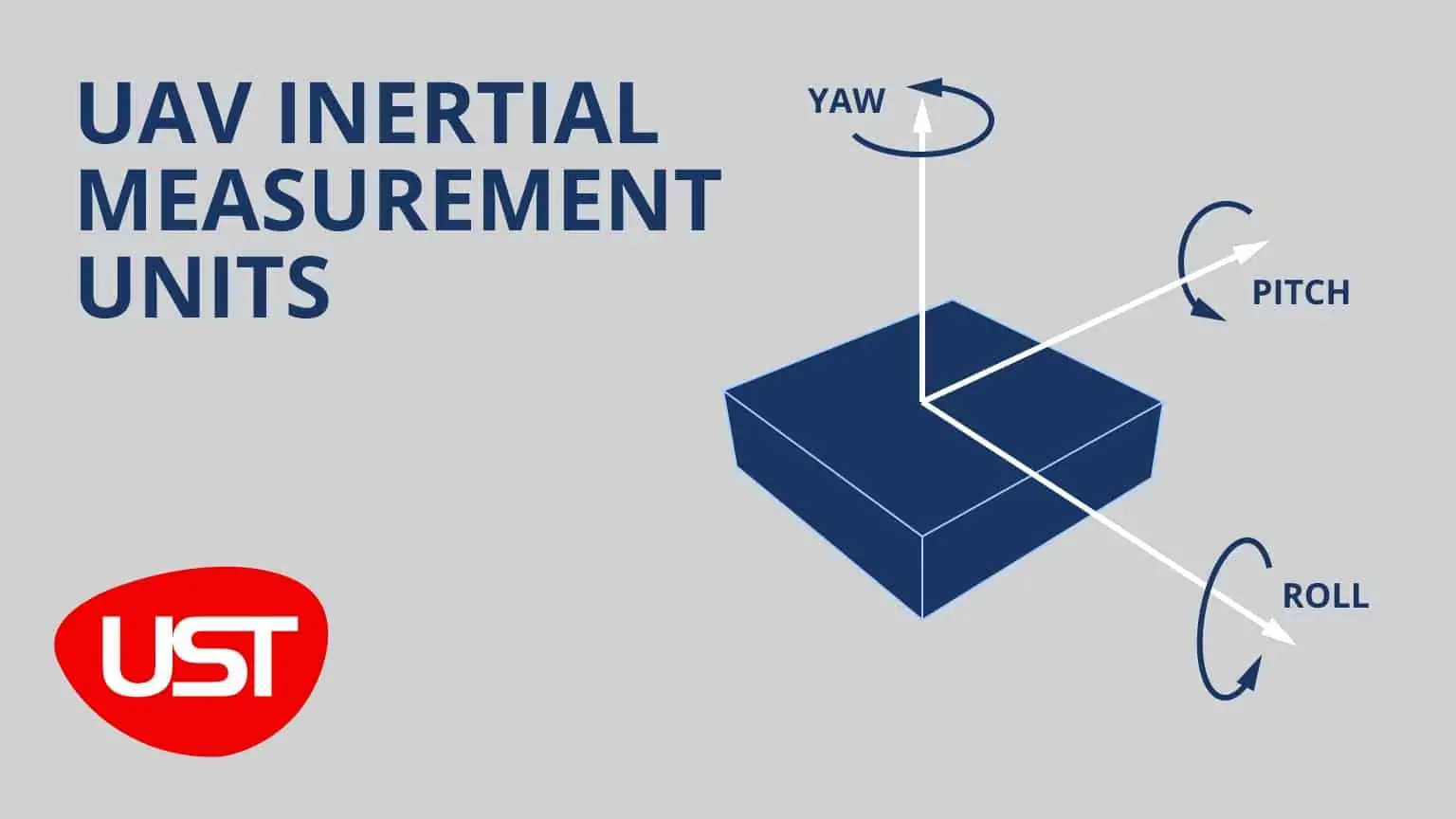
An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic device that uses accelerometers and gyroscopes to measure acceleration and rotation, which can be used to provide position data.
IMUs are essential components in unmanned aerial systems (UAVs, UAS and drones) – common applications include control and stabilization, guidance and correction, measurement and testing, and mobile mapping.
The raw measurements output by an IMU (angular rates, linear accelerations and magnetic field strengths) or AHRS (roll, pitch and yaw) can be fed into devices such as Inertial Navigation Systems (INS), which calculate relative position, orientation and velocity to aid navigation and control of UAVs.
IMUs are manufactured with a wide range of features, parameters, and specifications, so the most suitable choice will depend on the requirements for a particular UAV application. This article outlines some of the key options and considerations, such as the underlying technology, performance, and ruggedness, in selecting an IMU for drone-based applications. It also highlights some of the leading IMU manufacturers for UAS.
Inertial Measurement Unit Technologies
There are many types of IMU, some of which incorporate magnetometers to measure magnetic field strength, but the four main technological categories for UAV applications are: Silicon MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems), Quartz MEMS, FOG (Fiber Optic Gyro), and RLG (Ring Laser Gyro).

Advanced Navigation’s Motus MEMS IMU
Silicon MEMS IMUs are based around miniaturized sensors that measure either the deflection of a mass due to movement, or the force required to hold a mass in place. They typically perform with higher noise, vibration sensitivity and instability parameters than FOG IMUs, but MEMS-based IMUs are becoming more precise as the technology continues to be developed.
MEMS IMUs are ideal for smaller UAV platforms and high-volume production units, as they can generally be manufactured with much smaller size and weight, and at lower cost.
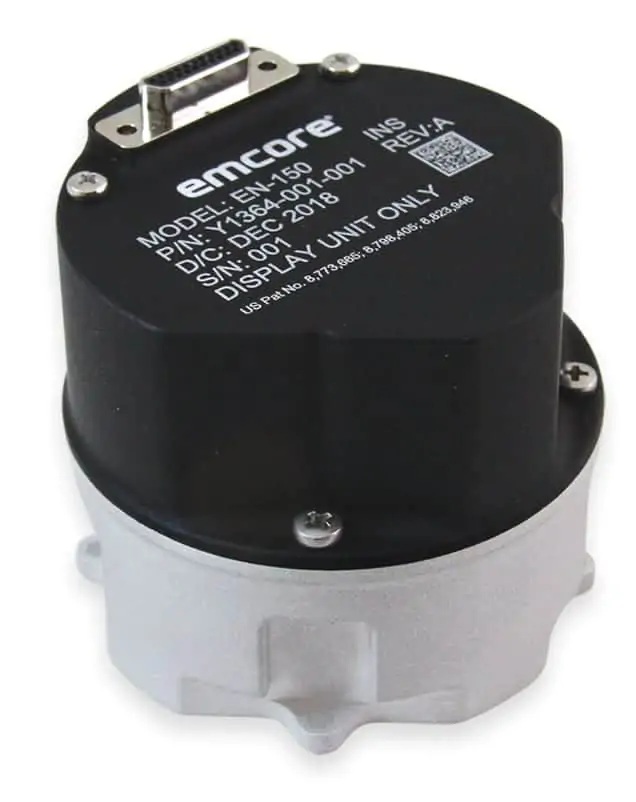

EMCORE’s EN-150 FOG IMU
FOG IMUs use a solid-state technology based on beams of light propagating through a coiled optical fiber. They are less sensitive to shock and vibration, and offer excellent thermal stability, but are susceptible to magnetic interference. They also provide high performance in important parameters such as angle random walk, bias offset error, and bias instability, making them ideal for mission-critical UAV applications such as extremely precise navigation.
Higher bandwidth also makes FOG IMUs suitable for high-speed platform stabilization. Typically larger and more costly than MEMS-based IMUs, they are often used in larger UAV platforms.
RLG IMUs utilise a similar technological principle to FOG IMUs but with a sealed ring cavity in place of an optical fiber. They are generally considered to be the most accurate option, but are also the most expensive of the IMU technologies and typically much larger than the alternative technologies.

The Systron Donner Inertial (an Emcore brand) SDI500 Quartz MEMS IMU
Quartz MEMS IMUs use a one-piece inertial sensing element, micro-machined from quartz, that is driven by an oscillator to vibrate at a precise amplitude. The vibrating quartz can then be used to sense angular rate, producing a signal that can be amplified and converted into a DC signal proportional to the rate. Quartz MEMS technology features high reliability and stability over temperature, and tactical-grade quartz MEMS IMUs rival FOG and RLG technologies for SWaP-C (size, weight, power and cost) metrics. These factors make it ideal for inertial systems designed for the space- and power-constrained environments of UAVs.
IMU Performance and Accuracy
The performance and accuracy of an IMU are influenced by a combination of factors, including the sensor technology, the thermal properties of the packaging, and the software used. The following parameters can be used when comparing the performance and accuracy of specific IMUs, to help determine suitability for a given UAV application:
- Bias – what does the IMU output read when the input is zero?
- Bias repeatability – how similar is the IMU bias when conditions have changed between measurements (e.g. for each powerup of the IMU)?
- Bias stability – how much does the bias change over time?
- Random Walk – how much random noise is present?
- Vibration Sensitivity – how much does the output of the angular rate change per unit of vibration present in the environment?
These factors are dependent on the technologies used in the IMU and the physical properties of the accelerometers, gyroscopes and magnetometers. If an IMU is manufactured with temperature compensation, this will improve the stability of the measurements.
For high-accuracy applications such as UAV surveying and mapping, a high data output rate is also important as this will reduce errors due to interpolation between readings.
IMU Performance Grades
In general, inertial sensors can be grouped into performance classes according to bias stability specifications which help to categorise the performance of a module. The higher the grade of sensor, the more accurate it tends to be.

Inertial Labs’ IMU-P Tactical Grade IMU
Typically, tactical- and industrial-grade IMUs are preferred for demanding applications such as UAV navigation, as they offer levels of high performance and accuracy.
Tactical-grade IMUs have gyroscopes with an extremely low in-run bias stability, meaning that the offset error is more stable over time. This is a necessary quality for mission-critical and high-precision applications such as UAV navigation and antenna and weapon platform stabilization.

VectorNav’s Industrial-Grade IMUs
Industrial-grade IMUs provide lower accuracy than tactical-grade-IMUs, but feature better performance and reliability than systems intended for consumer applications.
They offer good tolerance to shock and vibration, and exhibit good repeatability over time and temperature. Many industrial-grade IMUs are factory-calibrated to improve temperature performance.
MEMS-based IMUs are commonly used for industrial-grade applications, such as UAV platforms requiring small form factor components over other performance parameters for stabilization, control, and navigation.
In addition to consumer, industrial and tactical-grade IMUs, higher grades are also available: navigation-grade, and strategic or military-grade.
Rugged IMUs

Tactical Grade FOG IMU by Novatel
IMUs for UAVs will often need to be highly rugged in order to withstand demanding environments, such as high levels of shock and vibration, as well as wide temperature ranges. Enclosures may be made of materials such as precision-machined anodized aluminium, and be rated to various standards of ingress protection (environmental sealing) such as IP67, to provide protection from board stresses and hazards due to harsh environmental conditions.
IMUs with low vibration sensitivity provide higher accuracy navigation solutions in harsh UAV applications where vibration levels are high.
ITAR-Free IMUs
ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations)-free IMUs are not restricted by export controls that require a license to transfer any system around the world that contains ITAR-controlled technology. Using an ITAR-free IMU in an unmanned system design will simplify international sales of the final product.
IMUs that are designated as Significant Military Equipment (SME) and thus controlled by ITAR regulations include those specifically designed for unmanned aircraft that are also ITAR-controlled, as well as those designed for weapons or weapons systems.
Miniature IMUs
Size, Weight and Power requirements (SWaP) are key considerations in the design and development of UAV platforms, and many manufacturers aim to reduce the overall size and weight of their systems in order to fly greater distances, extend flight times, or increase payload capacity.
This has led many IMU suppliers to develop miniature IMUs with extremely low weight and small dimensions to meet the SWaP requirements of UAVs.
Choosing the right IMU
Engineers designing systems for UAV applications need to define and prioritize the performance, SWaP and cost factors that are most important to the success of their design in order to select the appropriate IMU and technology. Comparing IMUs based on their specific technologies and performance strengths and weaknesses will be a key factor of the design process.
The inertial sensor market spans an enormous range in terms of product price and performance; here is an overview of some of the leading IMU manufacturers:
SBG Systems

SBG Systems is a supplier of MEMS-based ITAR-free inertial sensors that balance cost, size and performance for unmanned systems applications.
The Ellipse 2 Micro Series is SBG’s smallest high-performance IMU, weighing in at 10 grams with a small form factor designed for SWaP-conscious unmanned systems. The IMUs can be interfaced with a GNSS receiver for increased accuracy position, heave and heading output. Learn more >
Inertial Labs
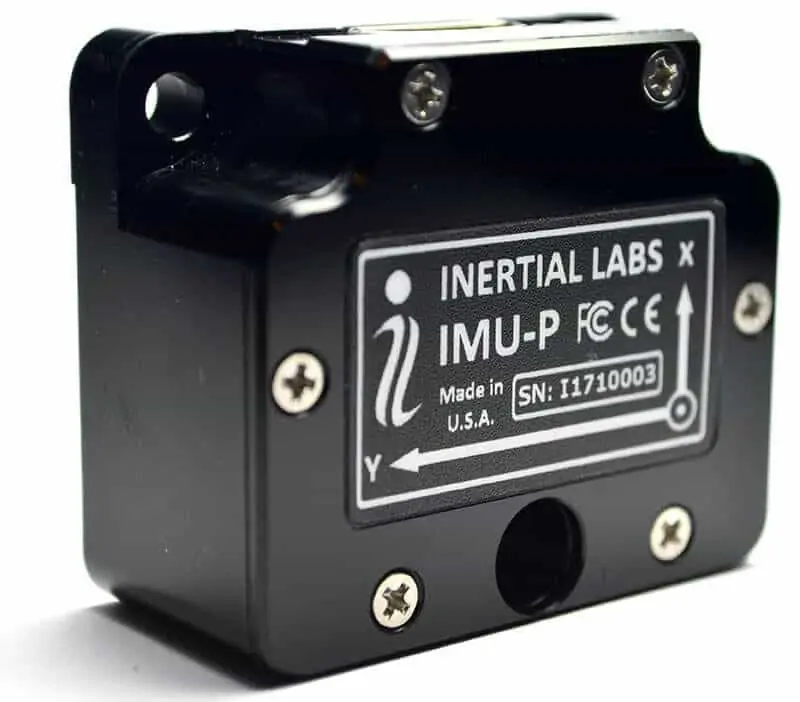

Inertial Labs develops high-performance MEMS-based inertial solutions with small size and low power requirements. The Inertial Labs IMU-P is an ITAR-free, fully temperature calibrated and compensated IMU that is available in industrial and tactical grades. It is designed for a variety of applications including navigation and control for UAVs.
Learn more >
Advanced Navigation
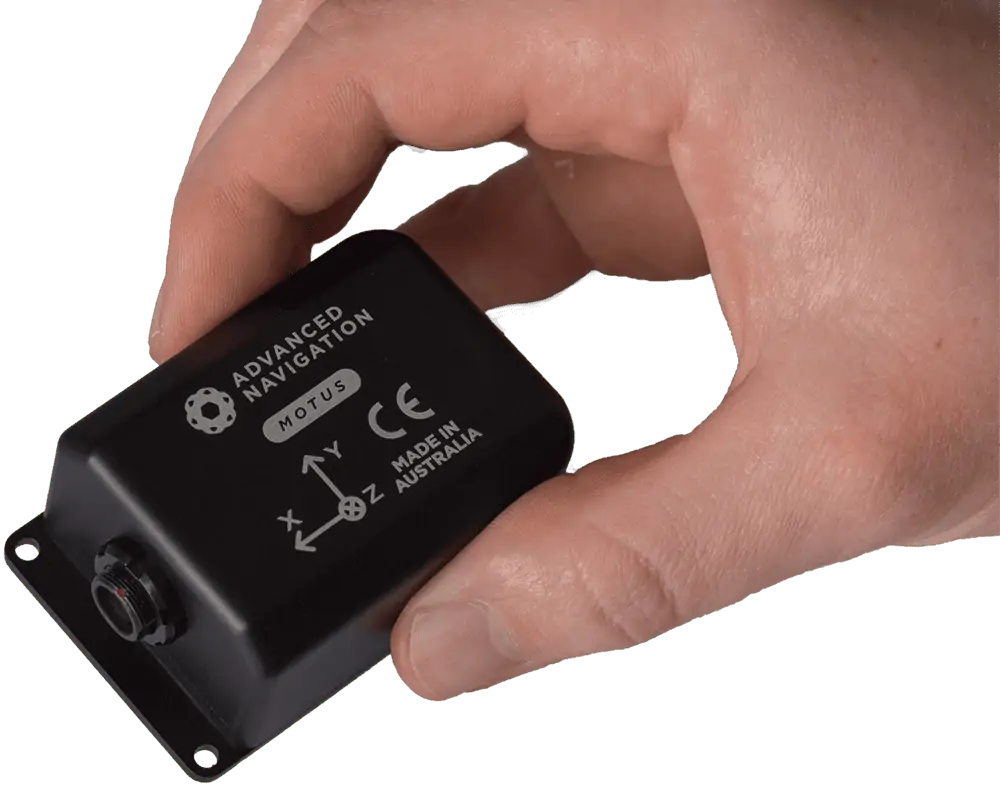

Advanced Navigation supplies MEMS and FOG-based navigation solutions for both commercial and military UAV applications. The Motus is a miniature ultra-high accuracy MEMS IMU that provides inertial performance exceeding that of even some FOG IMUs. It weighs in at just 26 grams, and features a bias stability of 0.4 °/hr. Learn more >
VectorNav Technologies
VectorNav Technologies is a developer of state-of-the-art MEMS tactical and industrial-grade sensors for demanding environments.
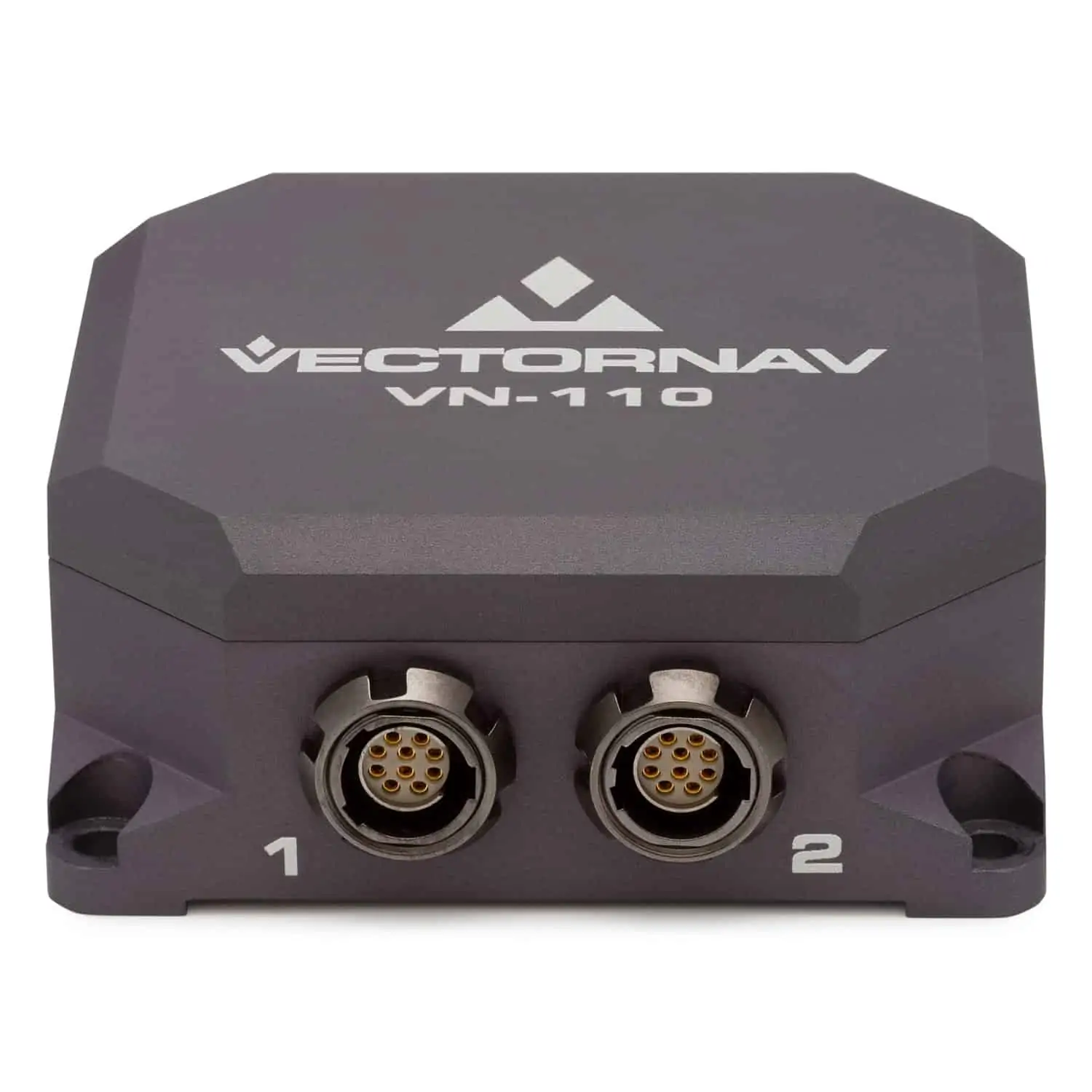

The VN-110 is a compact tactical-grade combination IMU/AHRS (Attitude & Heading Reference System) encased in a ruggedized aluminium housing. With less than 1˚/hr in-run gyro bias stability, its industry leading algorithms provide high-accuracy position, velocity, and attitude estimatesalong with compensated inertial measurements.

The VN-100 is a miniature industrial-grade IMU/AHRS, built on a high-performance, temperature-calibrated IMU core. It is available in both surface mount and rugged packaging options. Learn more >
EMCORE

EMCORE is a supplier of high-accuracy FOG IMUs that are designed with the low SWaP requirements of UAVS and unmanned systems in mind. The EN-150 is currently the smallest closed-loop FOG-based IMU available on the market, offering high accuracy and high performance.
The EN-300 is a low-noise, high-stability FOG IMU that provides the high performance required for GPS denied navigation, precise targeting and line-of-sight stabilization. It is available in three performance variants to suit a wide range of applications. Learn more >
Parker Hannifin, MicroStrain Sensing Systems
 Parker manufactures the MicroStrain line of inertial sensors – miniature inertial sensors designed for efficient integration into existing unmanned platforms. The 3DM-CV5-10 is a fully calibrated and temperature-compensated miniature industrial-grade IMU. Measuring 38 mm x 24 mm x 9.7 mm and weighing just 8 grams, it is Parker’s smallest, lightest and highest performance IMU in its class. Learn more >
Parker manufactures the MicroStrain line of inertial sensors – miniature inertial sensors designed for efficient integration into existing unmanned platforms. The 3DM-CV5-10 is a fully calibrated and temperature-compensated miniature industrial-grade IMU. Measuring 38 mm x 24 mm x 9.7 mm and weighing just 8 grams, it is Parker’s smallest, lightest and highest performance IMU in its class. Learn more >
NovAtel offers a range of IMUs from leading manufacturers, which can be coupled with a GNSS receiver to provide highly accurate and continuous position, velocity and attitude data. Available options include commercial MEMS IMUs, high-end tactical grade MEMS IMUs, tactical-grade FOG IMUs, and tactical-grade RLG IMUs. Learn more >
FIBERPRO
FIBERPRO develop tactical grade FOG-based Inertial Measurement Units for drones and Autonomous Vehicles, providing enhanced performance with improved linearity, reduced bias drift and cancelling of phase shift.
The FI 200C delivers high-accuracy velocity and angular rate data via a digital output. The closed-loop, ITAR- free IMU features a bias repeatability of less than 0.5 degrees/hour over the full temperature range. Learn more >
Gladiator Technologies
 Gladiator Technologies specializes in low-noise, high-performance MEMS-based IMUs for demanding environments. Their range of rugged IMUs feature environmental sealing, precision alignment and internal vibrational isolation, as well as bias, scale factor and misalignment modelling over the entire operating temperature range. Learn more >
Gladiator Technologies specializes in low-noise, high-performance MEMS-based IMUs for demanding environments. Their range of rugged IMUs feature environmental sealing, precision alignment and internal vibrational isolation, as well as bias, scale factor and misalignment modelling over the entire operating temperature range. Learn more >
Silicon Sensing
 Silicon Sensing manufactures high performance MEMS IMUs for an extensive range of unmanned applications. The IMU20 is an aerospace- and space-grade IMU capable of withstanding challenging high-impact, high-vibration environments. A medium grade, non-ITAR IMU for both commercial and industrial applications, it’s especially suited to UAVs, satellite launch platforms and more. Learn more >
Silicon Sensing manufactures high performance MEMS IMUs for an extensive range of unmanned applications. The IMU20 is an aerospace- and space-grade IMU capable of withstanding challenging high-impact, high-vibration environments. A medium grade, non-ITAR IMU for both commercial and industrial applications, it’s especially suited to UAVs, satellite launch platforms and more. Learn more >
Fizoptika Malta
 Fizopitika Malta specialise in ultra-miniature FOG (fiber optic gyroscope) sensor technologies, providing precision motion and orientation measurement in rugged, lightweight packages.
Fizopitika Malta specialise in ultra-miniature FOG (fiber optic gyroscope) sensor technologies, providing precision motion and orientation measurement in rugged, lightweight packages.
The non-ITAR U Series features the highly compact U183 and U121D, both designed to suit a broad range of unmanned inertial requirements and include a fully-integrated ADC board with RS422 serial communications, providing user-adjustable data rates of 0.1 to 4 kHz. Learn more >