Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) for Drones & UAV
Find Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) manufacturers and suppliers of drone SAR radar for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), including ISAR (Inverse) and InSAR (Inferometric), multi-mode radar for long-distance monitoringSynthetic aperture radar (SAR) uses radio or microwave pulses to capture 2D or 3D images of landscapes and other targets with finer resolution than conventional radar. The aperture of a radar antenna usually relates to its size; with SAR, the synthetic aperture refers to the distance that the SAR device moves during the time that the radar pulse is emitted and reflected. More distant objects therefore provide greater apertures, allowing for constant spatial resolution.
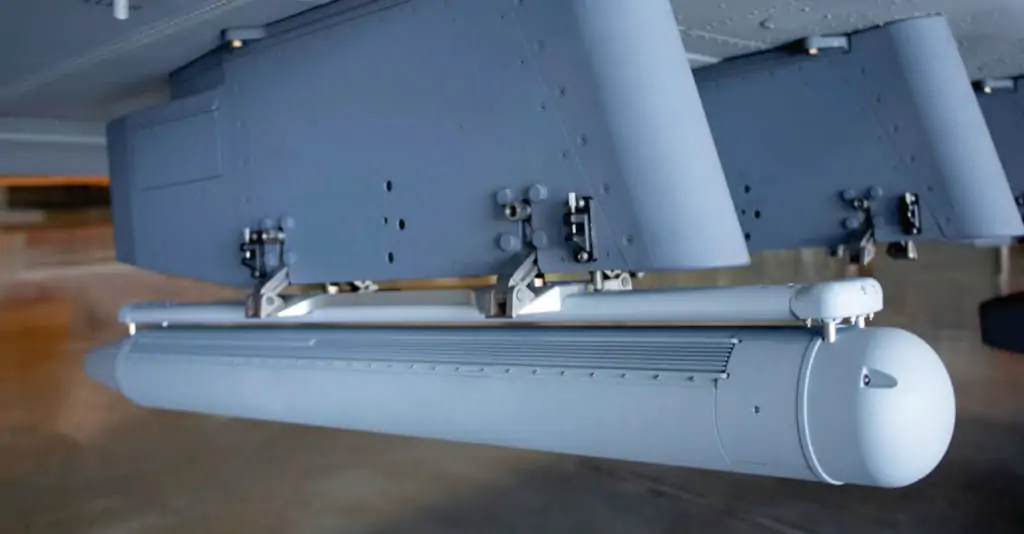
Low-SWaP UAV SAR
Low-SWaP (size, weight and power) SAR systems have been developed that are suitable for integration with UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles). Drone SAR imaging is used for a variety of applications, including geology and mineral exploration, battlefield reconnaissance and intelligence, and oil spill monitoring. Previously only used on large aerial platforms, UAV SAR payloads are small and compact enough for unmanned flight and able to provide advanced geospatial intelligence in all weather conditions.
Drone SAR Imaging
SAR provides a number of advantages over other imaging technologies. It can operate on frequencies that allow signals to not be attenuated by weather conditions, and can also operate during the day and at night. Designed for land and maritime operations SAR is also good at detecting metal objects not easily picked up by optical or thermal sensors, making it ideal for spotting targets such as vehicles and vessels.
Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar – ISAR
Additional remote sensing techniques involving SAR include inverse SAR (ISAR), in which the aperture is created by the movement of the target rather than the sensor. ISAR can be used to detect moving targets such as aircraft and ships.
Inferometric SAR – InSAR
Inferometric SAR (InSAR) uses multiple images of a target captured at different times to monitor changes in an area over time. It is often used for infrastructure and environmental monitoring.

























