Sense and Avoid (SAA) or Detect and Avoid (DAA) systems are technologies that allow unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones to integrate safely into civilian airspace, avoiding collisions with other aircraft, buildings, power lines, birds and other obstacles. These systems observe the environment surrounding the drone, decide whether a collision is imminent, and generate a new flight path in order to avoid collision.
UAV sense and avoid systems may combine data from a number of sensors, using sensor fusion algorithms, image recognition and artificial intelligence to provide the best outcome. Data is fed back to the drone flight controller, which can then decide on the best evasive manoeuvre or flight path correction to avoid collision.
BVLOS and Sense and Avoid Technology

Sagetech Mode S UAV Transponder
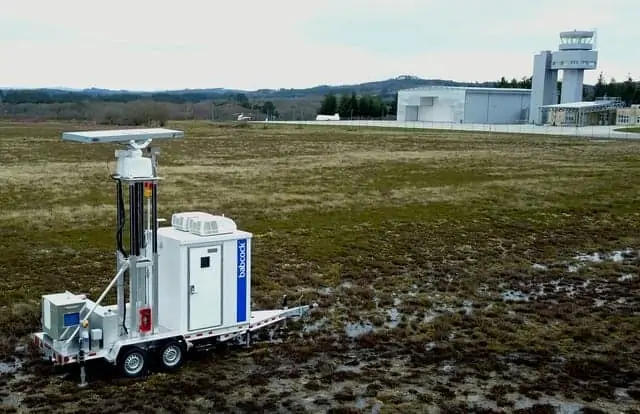
A reliable onboard sense and avoid system is crucial for obtaining a waiver for flight operations in many jurisdictions that typically otherwise require human observers or ground-based observation systems along the entire flight path. Sense and avoid systems are thus key to unlocking commercially viable BVLOS (beyond visual line of sight) drone operations that provide services such as inspection and cargo delivery over extremely long distances.
Co-operative Sense and Avoid Systems
Drones may use systems originally designed for manned aviation, such as TCAS (traffic collision and avoidance systems) or ADS-B (automatic dependent surveillance–broadcast), that periodically broadcast and receive identity, position and other information. This solution, however, relies on the co-operation of all aircraft within an airspace, and does not account for non-aviation obstacles.
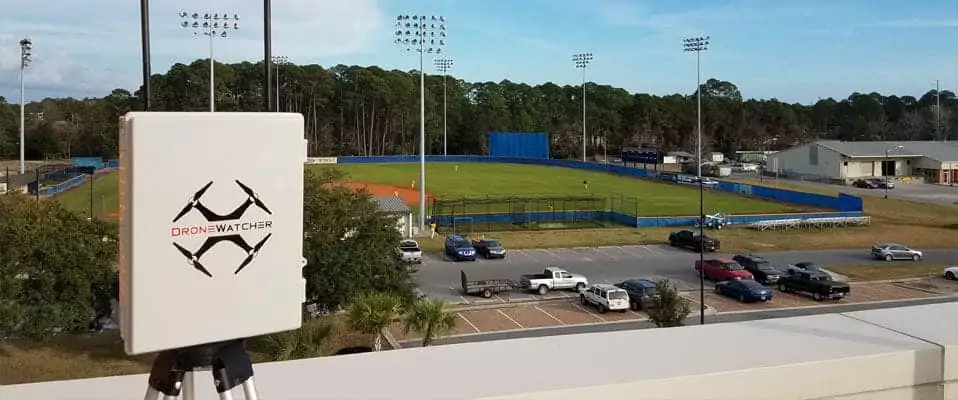

Active and Passive Detect and Avoid Solutions
Non-co-operative sensors for detect and avoid solutions can be divided into two groups – active and passive. Active sensors, such as radar, ultrasound and LiDAR, emit a signal which is then reflected by an obstacle and detected again by the sensor. Passive sensors detect a signal given off by the object itself, and include visual and infrared cameras. Non-co-operative sensors also provide an advantage in that they do not rely on a data link with another system to acquire information.
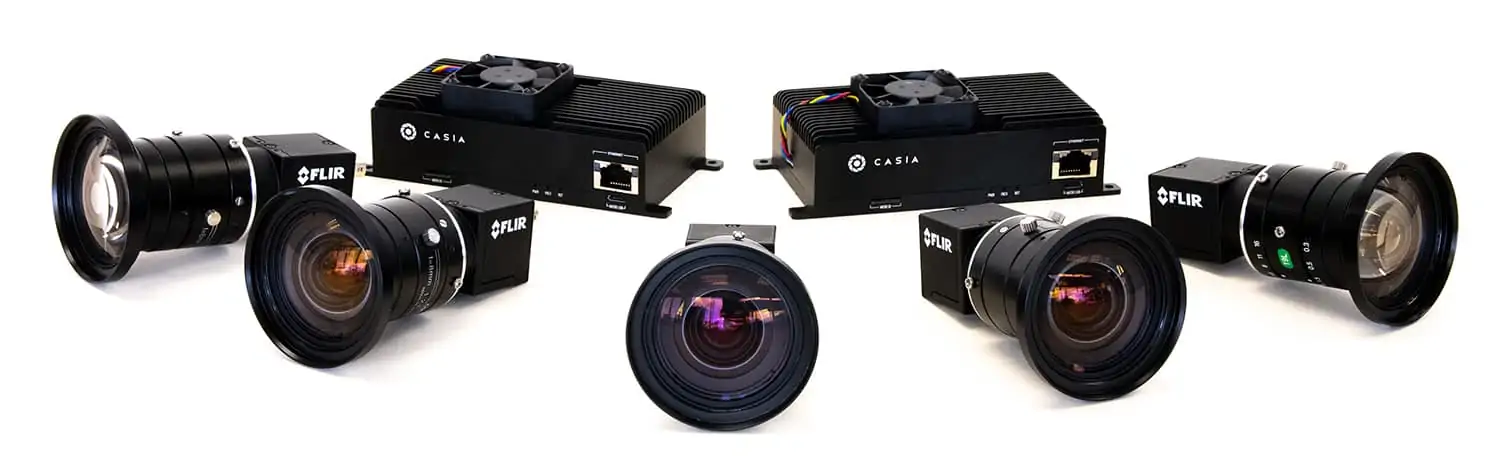

Active sensors can use time-of-flight information to provide accurate distance measurements to obstacles, which is extremely useful for rapid collision detection. However, they tend to be larger, heavier and require more power, making them unsuitable for integration into smaller, more SWaP (size, weight and power)-limited drones.
Passive sensors such as EO/IR (electro-optical/infrared) sensors are typically smaller, lighter, consume less power and can offer a very fast scan rate and high resolution. However, due to the lack of reflected signal measurement and time-of-flight data, their estimation of obstacle distances is less accurate. Their performance may also be affected by weather conditions.