Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. has further strengthened its FAZER R G2 industrial unmanned helicopter with the enhancement of its transport and delivery functions.
The company used the automatic navigation version of the model to bolster its response to the expansion of transportation and delivery requirements in the sector, such as material distribution in mountainous areas and longer-distance deliveries outside of the range of view.
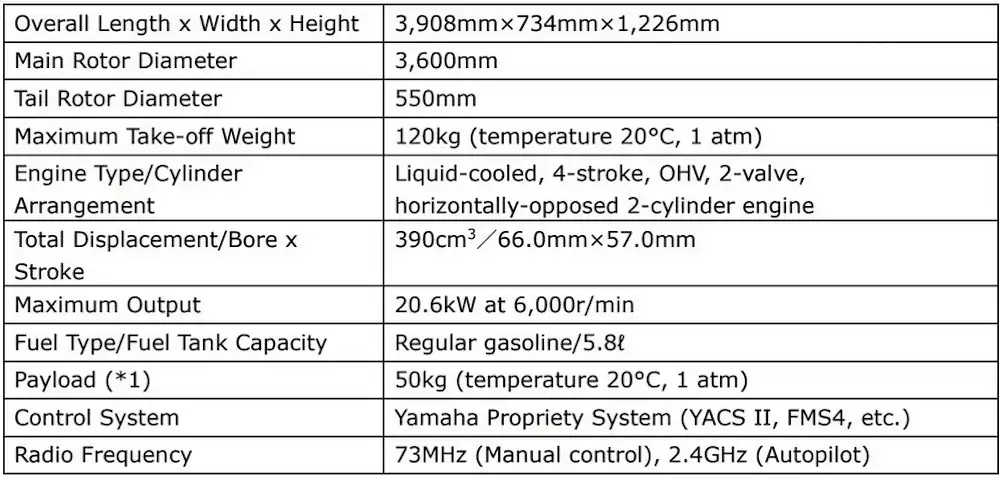
By changing the design and specifications of each part, such as increasing the diameter of the main rotor (rotor blade), FAZER R G2 achieves a maximum effective payload of up to 50kg depending on the usage environment, weather conditions, and altitude – a 15kg improvement on conventional models.
Solutions using industrial unmanned helicopters are expanding to a wider range of industrial environments such as the inspection of infrastructure including power transmission lines, surveying/observation, photography, and security.
The company has already put into practical use the transportation of power transmission line related materials by consignment for an electric power company, transported products from remote islands in collaboration with airline operators, and to mountainous areas in collaboration with home delivery companies.
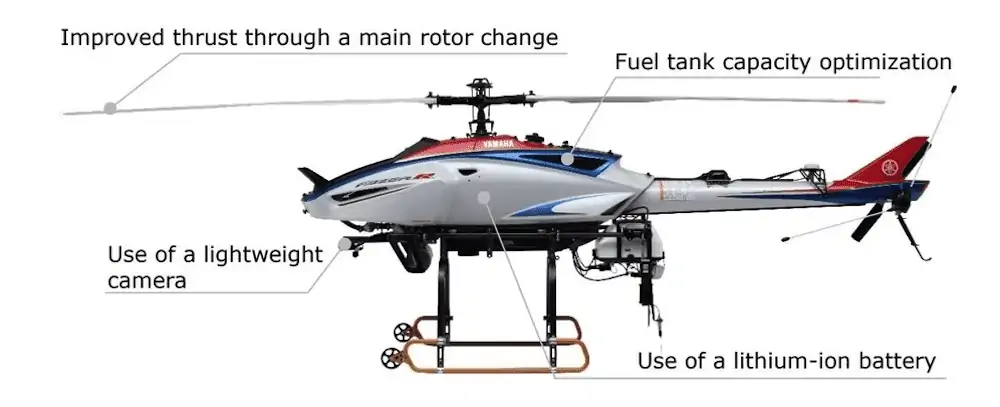

According to Yamaha, the payload is one of the functions that has the greatest impact on the efficiency of delivery operations. In the new FAZER R G2, the thrust is greatly improved through the adoption of a newly designed large main rotor. The rotor with a radius of 1.8m, where the conventional model was 1.56m, has been reshaped and includes excellent cooling performance along with thrust equivalent to an increase in payload of 10kg that is provided with the same output.
By optimizing the fuel tank capacity and adopting a lightweight camera and lithium-ion battery, the unit achieves a maximum payload of 50kg, which is 15kg more than the conventional model.
The conventional model required at least 29 flights to carry 1 ton of material, but the new model can complete the work in a minimum of 20 flights, contributing to a reduction of construction period requirements, costs, and labor.